38 thick skin labeled
5 layers of thick skin Thick Intergluteal Cleft And Lower Extremity Plaques | Dermatology jamanetwork.com. cleft intergluteal extremity jamanetwork. File:Adult Epidermis Histology 01.jpg - Embryology embryology.med.unsw.edu.au. epidermis histology skin layers system integumentary embryology human adult file anatomy edu labeled thin unsw med gland layer 400x medical Thin skin vs. thick skin: What is the difference? Thick skin is present on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands. This is because these areas receive more friction than other areas of the body, and thicker skin helps to protect from...
› pin › 369928556873635632Thick Skin - Labeled - Histology | Thick skin, Epidermis ... Thick Skin - Labeled - Histology Find this Pin and more on Histology - Skin by Summer Ekelund. More like this Langerhans Cell Epidermal Growth Factor Skin Grafting Layers Of The Epidermis Thick Skin Anatomy And Physiology Blood Cells Study A&P Chapter 5 Integumentary System flashcards. Play games, take quizzes, print and more with Easy Notecards. S

Thick skin labeled
Thick skin Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster noun Definition of thick skin : an ability to keep from getting upset or offended by the things other people say and do She has pretty thick skin when it comes to criticism. If you want to perform publicly, you'll need to grow a thicker skin. Learn More About thick skin Share thick skin Dictionary Entries Near thick skin thick shellbark thick skin mlpp.pressbooks.pub › chapter › thick-skin-tutorialThick Skin – Tutorial – Histology Atlas for Anatomy and ... Thick Skin - Tutorial 24. Unlabeled Integument Images 25. Quiz - Integument V. Muscle Tissues 26. Cardiac Muscle - Tutorial 27. Muscle - Tendon Connection - Tutorial 28. Neuromuscular Junction - Tutorial 29. Skeletal Muscle - Tutorial 30. Smooth Muscle - Tutorial 31. Unlabeled Muscle Images 32. Quiz - Muscle Tissue VI. Nervous System Tissues 33. What is the Difference Between Thick and Thin Skin 6 min read. The main difference between thick and thin skin is that thick skin is hairless and consists of a thick epidermis whereas thin skin contains hairs and its thickness varies based on the thickness of the dermis. Furthermore, thick skin exclusively occurs on the soles of feet, palms of hands, and the surface lining of the fingers and ...
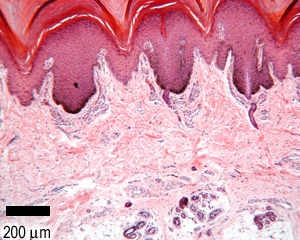
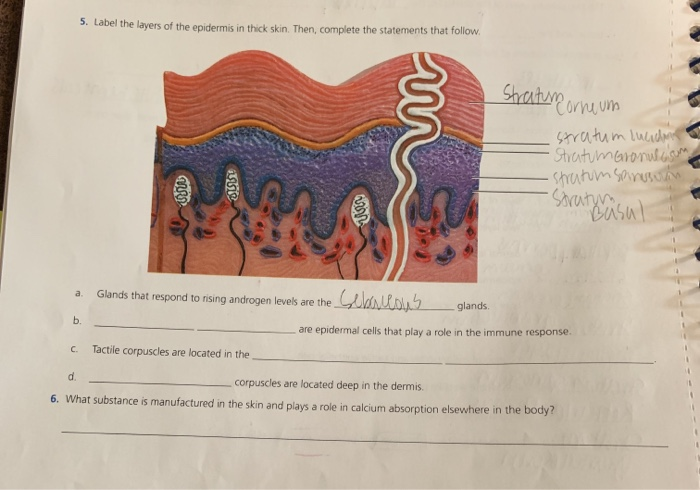
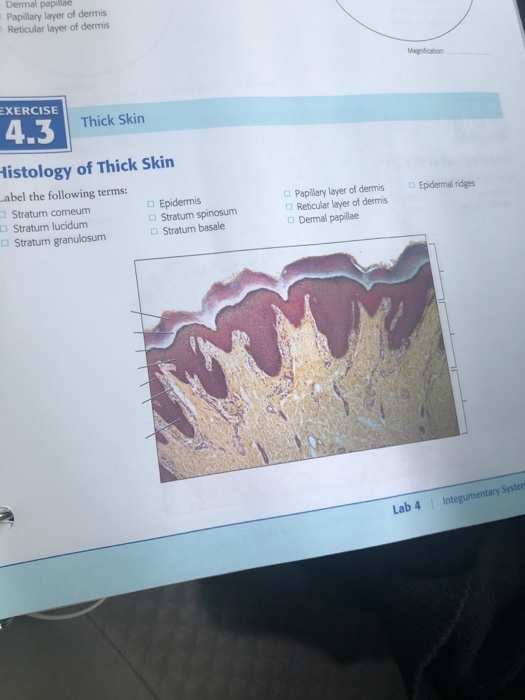
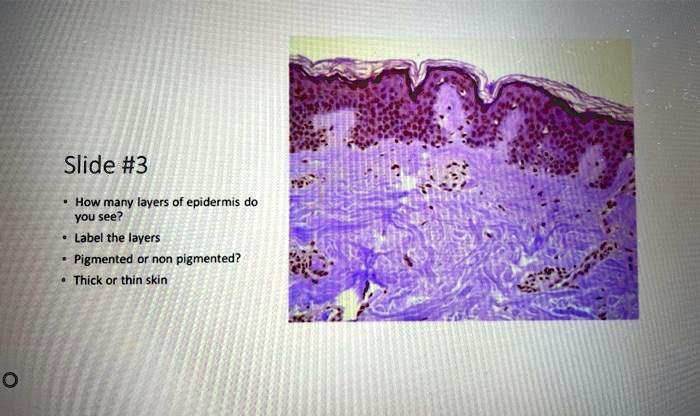
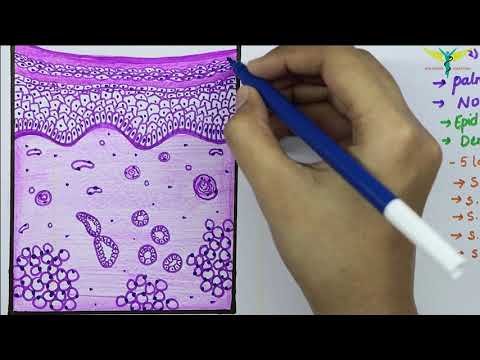
Thick skin labeled. photomicrograph of thick skin Diagram | Quizlet Start studying photomicrograph of thick skin. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Solved Procedure Microscopy of Thick Skin obtain a prepared | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: Procedure Microscopy of Thick Skin obtain a prepared slide of thick skin (which may be labeled "Palmar Skin"), and examine it with the naked eye to get oriented. Once you are oriented, place the slide on the stage of the microscope, and scan it on low power. You should be able to see the epidermis with its superficial layers of dead cells and the dermis with its pink ... Thick skin: location, structure, histology | Kenhub In areas where the skin is thick, the epidermal layer varies from 400 to 1400 μm. The skin is the thickest on the soles of the feet and palms of the hands. The thick skin has five layers of the epidermis in comparison to the thin skin which has four. These five layers include (deep to superficial): Basal layer Spinous layer Granular layer Anatomy, Skin (Integument) - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The skin is the body's largest and primary protective organ, covering its entire external surface and serving as a first-order physical barrier against the environment. Its functions include temperature regulation and protection against ultraviolet (UV) light, trauma, pathogens, microorganisms, and toxins. The skin also plays a role in immunologic surveillance, sensory perception, control of ...
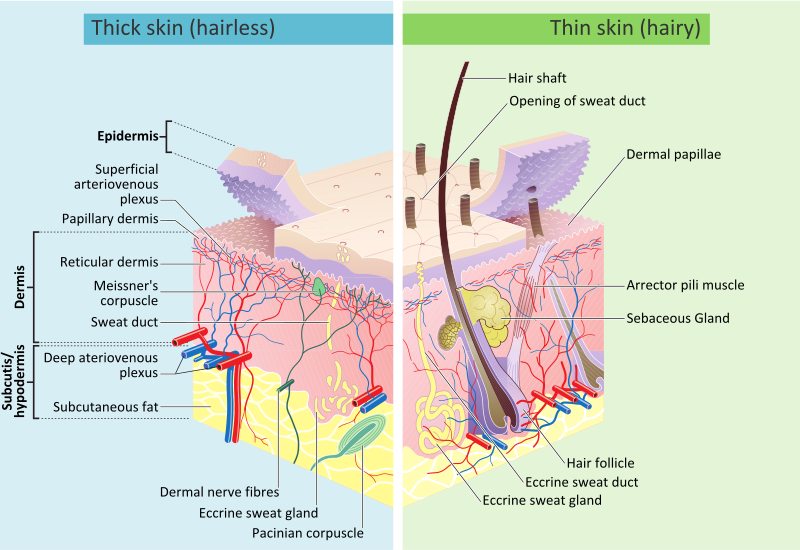
The Skin (Human Anatomy): Picture, Definition, Function, and Skin ... The skin is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and permits the ... Thin Vs. Thick Skin: Definitions, Differences, And Similarities Thin skin is present in all body parts except the hands, arms, and feet. It has a thinner top layer and does not have the stratum lucidum layer. Thick skin is hairless and does not contain sebaceous glands and apocrine sweat glands, whereas thin skin contains hair follicles and eccrine and apocrine sweat glands. Thick Skin - Histology Guide Thick Skin. Thick skin (>5 mm) covers the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The outer keratin layer is substantially thicker than in other parts of the body. Epidermis - stratified squamous keratinized epithelium divided into five strata (or layers). Solved Label the photomicrograph of thick skin | Chegg.com Question: Label the photomicrograph of thick skin . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
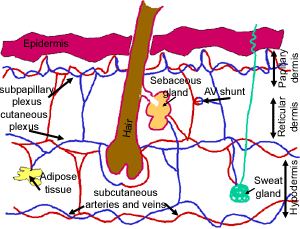
What is the difference between thick and thin skin? - The Handy Anatomy ... The terms thick and thin refer to the thickness of the epidermis. Most of the body is covered by thin skin, which is 0.003 inches (0.08 millimeters) thick. This skin contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and arrector pili muscles. The epidermis in thick skin may be six times thicker than the epidermis that covers the general body surface ... Skin: Cells, layers and histological features | Kenhub The thick, hairless skin in the palms and soles are therefore called glabrous skin, while skin elsewhere is referred to as hirsute (hairy) skin. Of note, the stratum lucidum is absent from hirsute skin but present in glabrous skin. Cell types Keratinocytes Keratinocyti 1/3 The epidermis is made up a variety of cell types. quizlet.com › 53167973 › integument-thick-skinIntegument: Thick skin -labeled slides Flashcards | Quizlet Brian Bich, Anatomy & Physiology I, Biology 1140, Lake Superior College, Slide images provided from Bish Epidermis (Outer Layer of Skin): Layers, Function & Structure While the epidermis is the thinnest layer of skin, the dermis is the thickest layer of skin. The dermis contains collagen and elastin, which help make it so thick and supportive of your skin's overall structure. All of your connective tissues, nerve endings, sweat glands, oil glands and hair follicles exist in the dermis as well as the ...
anatomylearner.com › skin-histology-slideSkin Histology Slide Identification - Thick and Thin Skin ... May 20, 2021 · Great, now, let’s try to identify the thick skin microscope slide with identifying points. #1. Presence of very thick epidermis that lines with keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. #2. The stratum corneum of epidermis is thicker. #3. The dermis layer shows dermal papillae and contains only sweat glands. #4.
Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Stratum lucidum, 2-3 cell layers, present in thicker skin found in the palms and soles, is a thin clear layer consisting of eleidin which is a transformation product of keratohyalin. Stratum corneum, 20-30 cell layers, is the uppermost layer, made up of keratin and horny scales made up of dead keratinocytes, known as anucleate squamous cells.
The Thickest and Thinnest Skin on the Body - Actforlibraries.org The thinnest skin on the body is that covering the eyelids, which is around 0.5 mm thick. This is an important reason why the skin on and around the eyelids becomes wrinkled before the rest of the body. Skin contains a protein called elastin. This provides the skin's elasticity, allowing it to return to its original position when displaced.
thick skin anatomy skin thick specimen medpics credit hist. Skin Layers, SEM - Stock Image P710/0441 - Science Photo Library . skin sem. Unlabeled Integument Images - Histology Atlas For Anatomy And Physiology mlpp.pressbooks.pub. unlabeled integument. Unit 11: The Integumentary System - Douglas College Human Anatomy pressbooks.bccampus.ca
Skin: The Histology Guide - University of Leeds Skin is the largest organ of the body. It has an area of 2 square metres (22 square feet) in adults, and weighs about 5 kilograms. The thickness of skin varies from 0.5mm thick on the eyelids to 4.0mm thick on the heels of your feet. Skin is the major barrier between the inside and outside of your body! Functions of skin
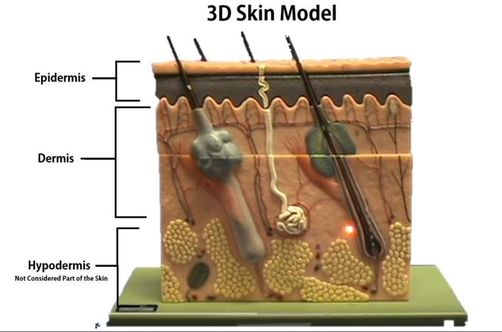
Integument- Thick Skin Model - MCCC Regions. Tissues. Layers of Epidermis. Thin Skin Slide. Thin Skin Model. Thick Skin Model
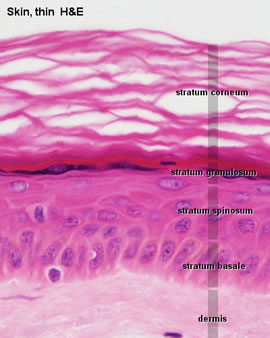
Skin: The Histology Guide Thick skin is only found in areas where there is a lot of abrasion - fingertips, palms and the soles of your feet. show labels This is a picture of an H&E stained section of the epidermis of thin skin. There are only four layers in the epidermis of thin skin. The stratum lucidum layer is absent.
Skin Anatomy: The Layers of Skin and Their Functions The skin is the body's largest organ. It is made of three layers, each of which has specific functions. The outermost epidermis is responsible for producing new skin cells, protecting the body from unwanted substances, and retaining moisture to keep the skin well hydrated. The middle dermis is responsible for supporting and strengthening the skin.
Difference Between Thin and Thick Skin Thick skin is lacking the sweat and sebaceous glands, and the hair follicles that are present in thin skin. However, thick skin does have a layer called the stratum lucidum, which is not found in thin skin. It occurs between the outermost layer of the epidermis, called the stratum corneum and a lower layer, called the stratum granulosum.
What is the Difference Between Thick and Thin Skin 6 min read. The main difference between thick and thin skin is that thick skin is hairless and consists of a thick epidermis whereas thin skin contains hairs and its thickness varies based on the thickness of the dermis. Furthermore, thick skin exclusively occurs on the soles of feet, palms of hands, and the surface lining of the fingers and ...
mlpp.pressbooks.pub › chapter › thick-skin-tutorialThick Skin – Tutorial – Histology Atlas for Anatomy and ... Thick Skin - Tutorial 24. Unlabeled Integument Images 25. Quiz - Integument V. Muscle Tissues 26. Cardiac Muscle - Tutorial 27. Muscle - Tendon Connection - Tutorial 28. Neuromuscular Junction - Tutorial 29. Skeletal Muscle - Tutorial 30. Smooth Muscle - Tutorial 31. Unlabeled Muscle Images 32. Quiz - Muscle Tissue VI. Nervous System Tissues 33.
Thick skin Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster noun Definition of thick skin : an ability to keep from getting upset or offended by the things other people say and do She has pretty thick skin when it comes to criticism. If you want to perform publicly, you'll need to grow a thicker skin. Learn More About thick skin Share thick skin Dictionary Entries Near thick skin thick shellbark thick skin



![Solved] Figure 4.2 Using the Above-Referenced Micrograph of ...](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4856/11ea30c9_727a_c682_a546_07f263a0459e_TB4856_00_TB4856_00_TB4856_00_TB4856_00_TB4856_00_TB4856_00_TB4856_00.jpg)




Epith_Skin_x63_001.jpg)


![Thick and thin skin structure [14]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Noe-Ortega-Quijano/publication/252859222/figure/fig2/AS:669995033956358@1536750672111/Thick-and-thin-skin-structure-14_Q320.jpg)










Post a Comment for "38 thick skin labeled"